
Networkmanager Introduction
Table of Contents
NetworkManager is a dynamic network configuration and control suite of tools designed to simplify managing network connections on Linux systems. It can handle all sorts of network connections such as wired, wireless, VPN, and most other types of configuration requirements.
The suite is composed of a main NetworkManager daemon service, and a number of client and utility programs. For the sake of an introductory talk I’ll only be referencing the nmcli and nmtui tools as well as nm-settings-nmcli but it’s important to understand there are more tools and utilities as part of the suite.
More details on NetworkManager and the full suite of tools can be found Here
The full listing of manual pages is found Here
NetworkManager - the daemon
The network manager daemon helps make network configuration and operation painless, automatic, and intuitive (once you understand the suite of tools!).
You can manage it like any other service if your system is using systemd
Command-line using nmcli
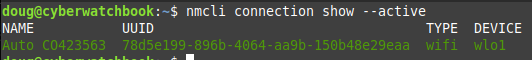
Showing active connections:
nmcli connection show --active
Show all the configuration settings for a provided connection:
nmcli connection show "demo-static"
To show the device status, and what network connection configuration is loaded for each device:
nmcli device show
You can also show device details for a specific device, such as eth0:
nmcli device show eth0
Now let us look at something a little more lengthy: setting up a new connection:
nmcli connection add con-name demo-static ifname eth0 type ethernet \
ipv4.method manual ipv4.dns 192.168.0.1 ipv4.addresses 192.168.0.10/24 \
ipv4.gateway 192.168.0.1
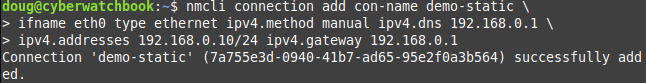
We can break this down to make it more understandable:
nmcli connection addis our base. It’s how we initiate adding a new connectioncon-name demo-staticis the alias forconnection.id demo-staticand sets what the human readable name for this connection will be.ifname eth0is the alias forconnection.interface-name eth0and sets which network interface the connection will be bound to.type ethernetis the alias forconnection.type ethernetand sets the type of connectionipv4is the base for all the related settings for ipv4 in our connection configuration:ipv4.methodsets the connection method such as “auto”, “manual” or “disabled”ipv4.dnssets the array of IP addresses of your DNS serversipv4.addressessets your IP addresses for the connection and prefix length. If more than one, you must separate them by a commaipv4.gatewaysets the gateway associated with the configuration.
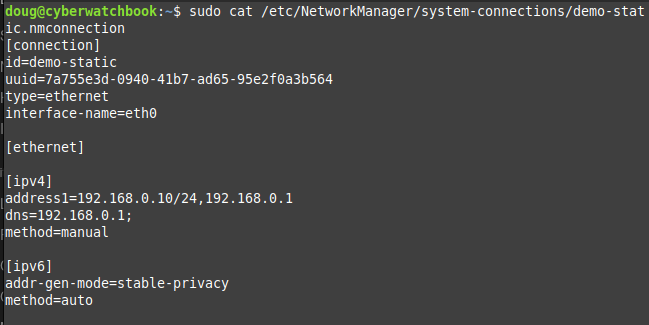
Now let’s see what that above command puts into the configuration file, that can be found here: /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/demo-static.nmconnection
To active a new connection configuration use the following command:
nmcli connection up demo-static
To verify the connection configuration is active:
nmcli connection show --active
You can always make changes by using the following command:
nmcli connection modify demo-static
For the full list of available options, it’s good to reference the nmcli man page, and the nm-settings-nmcli man page.
Configuration files
Interface configuration files can be found in the /etc/NetworkManager/system-connectons/ directory.
These files follow what’s referred to as “INI-style” which uses a key—value pair structure to organize the properties. This is similar to many other configurations file you may be used to, such as YAML or TOML.
Example network configuration file:
$ cat /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/'System eth0.nmconnection'
[connection]
id=System eth0
uuid=1b1e227f-bc91-44ef-8bae-5af3b347f9f1
type=ethernet
interface-name=eth0
timestamp=1709816444
[ethernet]
mac-address=00:16:76:6C:AA:DD
[ipv4]
address1=192.168.0.9/24,192.168.0.254
dns=192.168.0.1;
dns-search=dns.local.example.com;
method=manual
[ipv6]
method=ignore
Configuration file options
To look through all the configuration file options available, you can check the manual page for nm-settings-nmcli with the following:
man nm-settings-nmcli
While this file is a reference to using the nmcli command to configure network settings, it is also a good reference in general for all the options that you can configure.